Donald Corenman MD demonstrates a surgical removal of a far lateral disc herniation in the lumbar spine using a minimally invasive surgical technique.
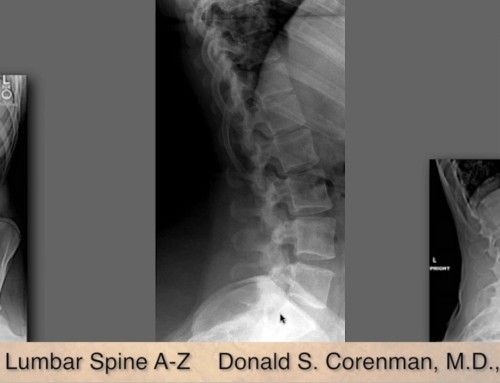
95% of disc herniation in the lumbar spine occurs posterolaterally and compress the nerve in the canal. Herniations are so common in the lumbar spine because the walls of the disc are thinner and therefore weaker. Only 2-5% of the time, a disc herniation occurs on the far lateral position – the spine outside the spinal canal. Typical symptoms include buttocks and leg pain, along with increased pain while standing.
Treatment for far lateral herniation is through an incision about 3 cm off the midline and splits the erector spinae muscle (the muscle that causes the spine to bend backwards). Since the fibers of the muscles run in line with the incision, this approach is not significantly traumatic. The spinal canal is not entered and the fragment is removed from the side of the spine.